The U.S. inflation rate reflects how prices for goods and services increase year-over-year, influenced by economic cycles of expansion and contraction. The Federal Reserve aims to keep Inflation at a 2% annual rate, using monetary policy to maintain stability.
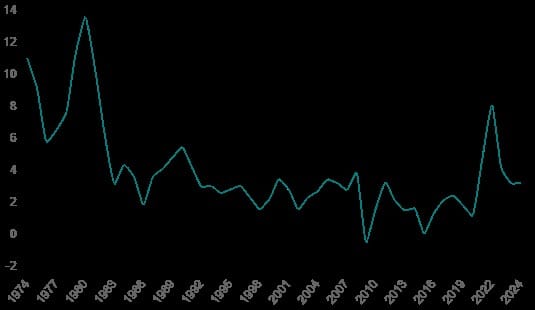
Over the past 50 years, inflation trends have been shaped by events like the oil crises of the 1970s, the stabilization policies of the 1980s, the tech boom of the 1990s, the 2008 financial crisis, and the recent COVID-19 pandemic. This blog explores these trends from 1974 to 2024, examining their impact on the economy and consumers.
Understanding Inflation
To comprehend Inflation's impact on staple prices, it's essential to understand Inflation, its causes, and how it is measured. This section will provide a foundational overview of Inflation and its mechanisms.
Inflation is the overall rise in the prices of goods and services within an economy over time. This reduces the purchasing power of money, meaning consumers can buy less with the same amount of money.
Causes of Inflation
Various factors can drive inflation, each affecting the economy in distinct ways. These factors include demand-pull Inflation, cost-push Inflation, and built-in Inflation.
- Demand-Pull Inflation: This occurs when the demand for goods and services surpasses their supply, causing prices to rise.
- Cost-Push Inflation: This happens when production costs increase, prompting producers to raise prices to maintain profit margins.
- Built-in Inflation (Wage-Price Inflation): This occurs when workers demand higher wages to cope with rising living costs, leading to increased production costs and, subsequently, higher prices.
How Inflation is measured
Inflation is measured using indices that monitor price changes over time. The most commonly used indices are the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Producer Price Index (PPI).
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): This index tracks the average price change that consumers pay for a specific basket of goods and services over time.
- Producer Price Index (PPI): This index measures the average change in selling prices that domestic producers receive for their output.
Historical Perspective - Staple Prices 50 Years Ago
The 1970s was a decade marked by economic turbulence, including the 1973 oil crisis, which led to high inflation rates and significant price increases for various goods. The economic environment was characterized by stagflation, where high Inflation coexisted with stagnant economic growth and high unemployment.
Key Factors Influencing Prices 50 Years Ago
Several factors contributed to the price levels 50 years ago, including the oil embargo, high wage demands, and increased government spending.
● Oil Embargo and Energy Crisis: OPEC's 1973 oil embargo led to a significant increase in oil prices, affecting transportation and production costs across the economy.
● High Wage Demands and Labor Strikes: Workers demanded higher wages to keep up with rising living costs, contributing to cost-push Inflation.
● Increased Government Spending: Expansionary fiscal policies stimulating economic growth also fueled Inflation.
Current Perspective - Staple Prices in 2024
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the inflation rate in the USA is approximately 3.0% annually as of July 2024. Various factors influence this rate, including the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, supply chain disruptions, and fluctuating energy prices.
Key Factors Influencing Prices in 2024
Several key factors influence today's prices, including supply chain issues, rising energy costs, and government policies.
● Supply Chain Issues and Logistical Bottlenecks: Ongoing supply chain disruptions due to global events and increased demand have led to shortages and higher prices for many goods.
● Rising Energy and Raw Material Costs: Fluctuations in oil prices and increased demand for renewable energy sources have contributed to higher production costs.
● Government Policies and Stimulus Measures: Stimulus packages and increased government spending to support economic recovery have also impacted inflation rates.
Comparative Analysis of Staple Prices (50 Years Ago vs. 2024)
Comparing staple prices from 50 years ago to today provides a clear picture of how Inflation has affected the cost of essential goods. This section presents a detailed comparison of vital staple prices across these two periods.
Side-by-Side Comparison of Staple Prices Over 50 Years
To illustrate the impact of Inflation over the past five decades, we compare the prices of everyday staples 50 years ago and in 2024.
|
Staple |
Price 50 Years Ago (USD) |
Price in 2024 (USD) |
Percentage Increase (%) |
|
Milk
(gallon) |
$1.57 |
$3.89 |
147.13% |
|
Bread
(loaf) |
$0.28 |
$2.50 |
792.86% |
|
Eggs
(dozen) |
$0.78 |
$3.25 |
316.67% |
|
Ground
Beef (lb) |
$0.98 |
$6.00 |
512.24% |
|
Gasoline
(gallon) |
$0.53 |
$3.80 |
617.92% |
Impact of Global Events
Global events significantly impact Inflation and prices. The oil crises and the COVID-19 pandemic have caused supply disruptions and increased production costs.
Significant global events such as the oil crises of the 1970s and the COVID-19 pandemic have profoundly affected Inflation and staple prices. These events cause supply disruptions, increased production costs, and shifts in consumer behavior, all contributing to price volatility.
Inflation's Broader Economic Impact
Inflation doesn't just affect prices; it has broader economic implications. This section examines how Inflation impacts purchasing power, savings, investments, wages, and interest rates.
How Inflation Affects Purchasing Power
As prices rise, money's purchasing power decreases. Consumers need more money to buy the same amount of goods and services, leading to a higher cost of living.
Impact on Savings and Investments
Inflation erodes the value of savings, making it crucial for individuals to invest in assets that can outpace Inflation. Assets such as stocks, real estate, and inflation-protected securities can help preserve value.
Effect on Wages and Employment
Inflation can lead to higher wage demands as workers seek to maintain their standard of living. However, if wage increases outpace productivity gains, it can result in higher production costs and further Inflation.
Influence on Interest Rates
Central banks like the Federal Reserve may raise interest rates to combat high Inflation. Higher interest rates can slow economic growth by making borrowing more expensive, impacting consumer spending and business investments.
Impact on Future Dollars
Looking ahead, Inflation will continue to shape the value of money and the cost of goods. This section projects future inflation rates, estimates staple prices in the coming decade, and discusses strategies to mitigate Inflation's impact.
Projected Inflation Rates for the Next Decade
Economists project moderate inflation rates over the next decade. Technological advancements, demographic changes, and fiscal policies influence these projections. The projected average annual inflation rate is around 2.5% to 3.5%, depending on economic conditions and policy decisions.
Estimation of Future Staple Prices Based on Current Trends
Assuming a consistent inflation rate, staple prices are expected to continue rising. Here's an estimation of future staple prices in 2034:
|
Staple |
Projected Price in 2034 (USD) |
|
Milk
(gallon) |
$5.50 |
|
Bread
(loaf) |
$3.75 |
|
Eggs
(dozen) |
$4.75 |
|
Ground
Beef (lb) |
$8.50 |
|
Gasoline
(gallon) |
$5.25 |
Analysis of the Future Value of Today's Dollars
If Inflation continues at its current pace, the value of today's dollars will decrease significantly over the next decade. This underscores the importance of investing in inflation-protected assets and adopting financial strategies to preserve purchasing power.
Strategies for Mitigating the Impact of Inflation
● Diversify Investments: Spread investments across various asset classes to hedge against Inflation.
● Invest in Real Assets: Real estate, commodities, and other tangible assets often appreciate Inflation.
● Adjust Savings Plans: Consider inflation-protected securities and high-yield savings accounts.
● Monitor Expenses: Regularly review and adjust household budgets to manage rising costs effectively.
How Reachfi Can Help
Understanding and planning for Inflation is crucial for financial stability. Reachfi provides tools and resources to help individuals and households manage their finances effectively in the face of rising prices. By offering financial modeling and scenario planning features, Reachfi enables users to explore various what-if scenarios, helping them make informed decisions about their spending, savings, and investments. This proactive approach can mitigate the impact of Inflation on purchasing power and overall financial health.
Conclusion
Inflation has profoundly impacted staple prices in the USA over the past 50 years, significantly increasing the cost of essential goods. Understanding the factors driving Inflation, such as supply chain disruptions, energy prices, and government policies, is crucial for effective financial planning. By staying informed and adopting proactive strategies, households can better manage the inflation challenges. As Inflation continues to shape the economic landscape, planning and investing wisely is essential to preserve purchasing power and ensure financial stability.
